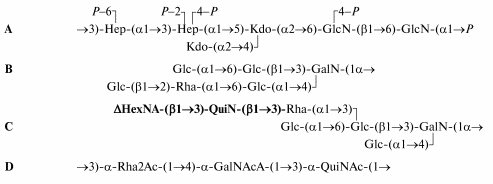Elucidation of the Structure of the Lipopolysaccharide Core and the Linkage between the Core and the O-Antigen in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Immunotype 5 Using Strong Alkaline Degradation of the Lipopolysaccharide
O. V. Bystrova1, A. S. Shashkov1, N. A. Kocharova1, Y. A. Knirel1*, U. Zähringer2, and G. B. Pier3
1Zelinsky Institute of Organic Chemistry, Russian Academy of Sciences, Leninsky pr. 47, Moscow, 119991 Russia; fax: (095) 135-5328; E-mail: knirel@ioc.ac.ru2Research Center Borstel, Center for Medicine and Biosciences, Parkallee 22, Borstel, D-23845 Germany
3Channing Laboratory, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, 181 Longwood Ave., Boston, MA 02115, USA
* To whom correspondence should be addressed.
Received November 18, 2002; Revision received January 8, 2003
The products of the strong alkaline degradation of the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa immunotype 5 were separated by anion-exchange HPLC and studied by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and NMR spectroscopy. It was found that two major products have the same inner core region and lipid A carbohydrate backbone (A) but different outer core regions (B and C). The difference is in the position of a rhamnose residue, which is substituted with either an additional glucose residue (B) or a disaccharide remainder of the degraded O-polysaccharide (C). The site and the configuration of the linkage between the O-polysaccharide and the core were determined and, together with published data, the structure of the so-called biological repeating unit of the O-antigen was defined (D). The glycosidic linkage of the quinovosamine residue is beta when it links the O-polysaccharide to the core (C) and alpha when it connects the interior repeating units of the O-polysaccharide to each other (D).In the structures shown Rha stands for rhamnose, Kdo for 3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonic acid, Hep for L-glycero-D-manno-heptose, GalNAcA for 2-acetamido-2-deoxygalacturonic acid, QuiN for 2-amino-2,6-dideoxyglucose (quinovosamine), DeltaHexNA for 2-amino-2-deoxy-D-threo-hex-4-enuronic acid; all monosaccharides are in the pyranose form and have the D configuration, except for Rha and GalNAcA that have the L configuration. In C, the remainder of the degraded O-polysaccharide is shown in bold type.
KEY WORDS: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, lipopolysaccharide, core oligosaccharide, repeating unit, O-antigen